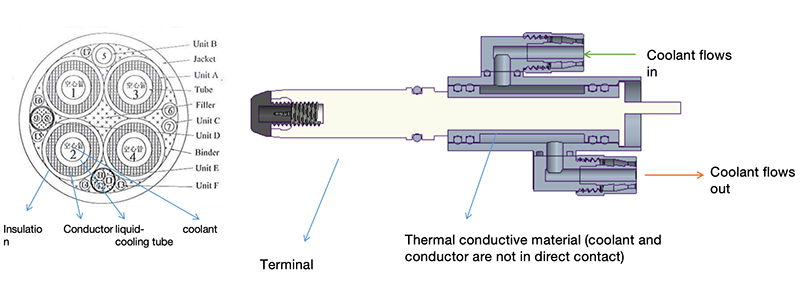
Liquid cooled CCS2 EV Charging Cable Description
Liquid cooled CCS2 EV Charging Cable
| Item Name | CHINAEVSE™️Liquid cooled CCS2 EV Charging Cable | |
| Standard | IEC 62196-2014 | |
| Rated voltage | 1000VDC | |
| Rated Current | 250~500A | |
| Certificate | TUV, CE | |
| Warranty | 5 Years | |
Liquid cooled CCS2 EV Charging Cable Components
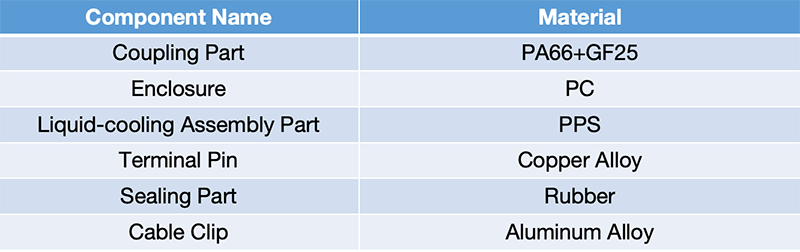
System Control Scheme
Forced convection cooling is used at the oil inlet pipe of the tank, and the speed of the fan and pump will be regulated by voltage of 0~5V. The system flow and pressure are monitored by a flow meter and a pressure gauge. The flow meter and pressure gauge can be placed at the oil inlet or outlet pipe.
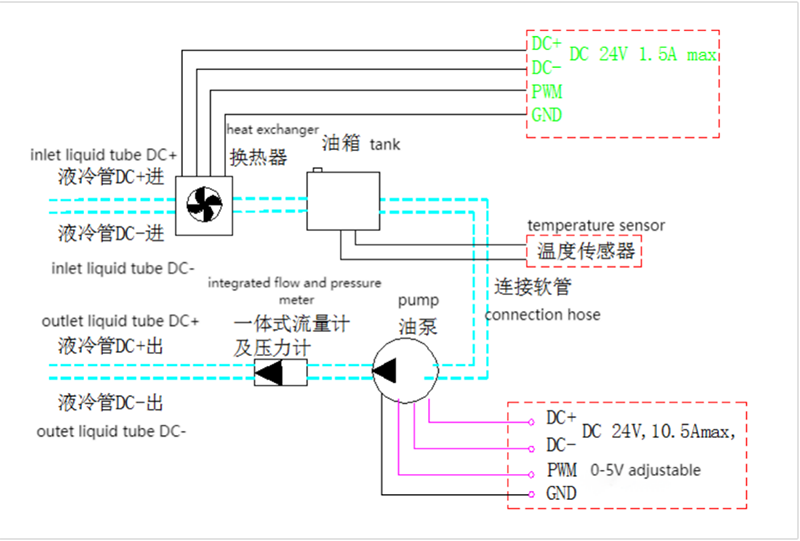
Liquid cooled CCS2 EV Charging Cable Specification
Coolant Selection
The coolant of liquid-cooled EV charging cables can be divided into oil and water.
Oil-cooling:Insulated, oil (dimethyl silicone oil) can directly contact the terminals and has good heat transfer efficiency, so it has been widely used. But simethicone is not biodegradable.
Water-cooling:The terminals are not in direct contact with the coolant (water+ethylene glycol solution) , so heat exchange relies on thermal conductive materials, as a result the cooling effect is limited. However, it is biodegradable and widely used in regions such as Europe where coolant biodegradability is more emphasized.
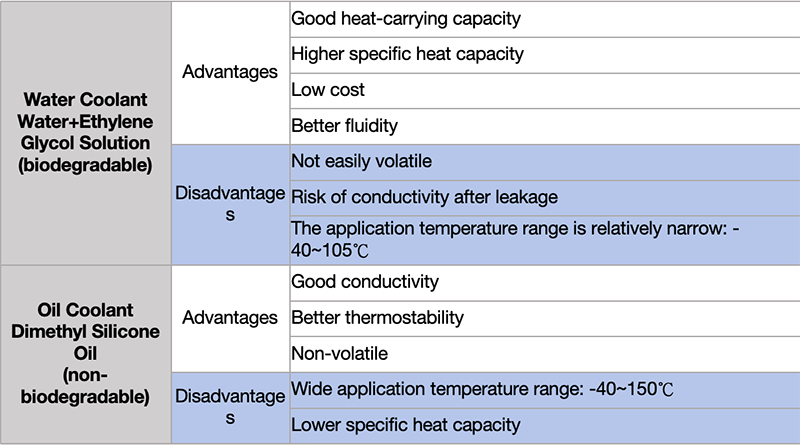
When the coolant is water + ethylene glycol solution, due to the conductivity of water, the coolant cannot be in direct contact with metal conductors.
A copper-hugging water structure should be adopted as the cable structure. The conductor at the terminals rely on insulating materials with certain thermal conductivity to conduct heat with the coolant.